Heart attacks don’t always cause chest pain
Crushing chest pain is often considered the telltale sign of a heart attack, but it’s far from the only one, and it might not be present at all.


Unfortunately, this isn’t widely known, so many people miss the subtler symptoms of a heart attack - such as dizziness, nausea and shortness of breath - often with tragic results.
You shouldn’t tilt your head back when you have a nosebleed
The common advice for people suffering from a nosebleed is to tilt their head back and pinch the bridge of their nose.


Not only will this do precisely nothing to help the nosebleed, it can also result in swallowing blood, which - with a severe enough bleed - can cause choking.
It’s more complicated than “good” and “bad” cholesterol
There are two types of cholesterol - HDL (high-density lipoprotein) and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) - which generally get labelled as “good” and “bad” respectively.


Recent research has shown that these descriptions are actually misleading, and HDL can still cause health problems if blood levels get too high.
You shouldn’t stop taking antibiotics when you feel better
Antibiotics can come with nasty side effects, so people often stop taking them as soon as they feel better, even if they haven’t finished the course.
In addition to increasing the risk of rebound infections, stopping your course of antibiotics too soon can lead to superbugs like MRSA.
You shouldn’t starve a fever
The advice to “feed a cold, starve a fever” has no bearing in medical science, and - in addition to being wrong - it’s also potentially harmful.
When you’re ill, your body needs nutrients to give it the energy to recover, no matter what your symptoms are.
You don’t get sick from being cold
Since rates of cold and flu increase during winter, many people make the logical assumption that being cold can make you sick.


However, rates of infection actually rise during winter months not because of the temperature, but because people spend more time indoors together, increasing the likelihood of passing on viruses.
Men aren’t more at risk of heart disease
Heart disease is often portrayed as a condition that only men need to worry about, but the statistics tell a different story.
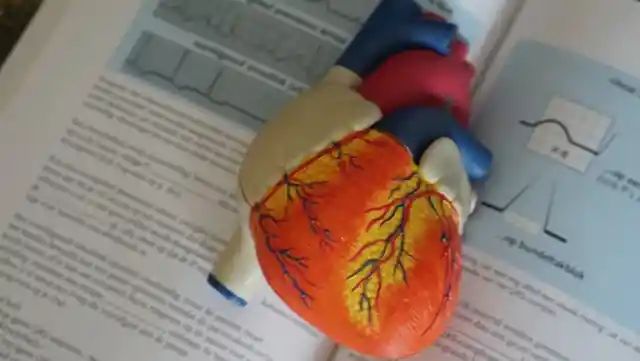

In the United States, heart disease is the leading killer of both men and women, and women are actually more likely than men to die from a heart attack.
You can’t cure mental illness by being positive
Telling someone suffering from depression, anxiety or other mental health problems to “snap out of it” or “just try to be happier” isn't only wildly insensitive; it’s also dangerous.


Perpetuating the myth that you can overcome mental illness through willpower and positive thinking reduces the likelihood that sufferers will seek the professional help that could actually help them recover.
Vomiting isn’t a symptom of the flu
It’s widely believed that vomiting is a sign you’ve got the flu, rather than just a case of the common cold.


In reality, neither infection generally causes vomiting. If you’ve got flu-like symptoms and you’re throwing up, you’ve probably got a case of gastroenteritis, which requires different treatment options.
You can actually die of a broken heart
While the grief that follows a breakup or the loss of a loved one can be unbearably painful, you probably think that it can’t actually kill you.


However, a number of studies have shown that the risk of heart attack rises by about 50% when you’re grieving, a phenomenon which scientists have dubbed “stress-induced cardiomyopathy.”
You shouldn’t keep a person with concussion awake
People who’ve sustained a concussion are often advised not to go to sleep, even if they’re feeling tired. This, however, is a mistake.


Recent studies have shown that sleep is incredibly important when it comes to recovering from a traumatic head injury, as it gives the brain a chance to start healing.
You shouldn’t take antibiotics if you have the flu
Antibiotics are specifically designed to treat bacterial infections, and they have no effect on viruses. This means that they shouldn’t be taken to treat a cold or flu.


Unfortunately, many people still reach for antibiotics when they’re suffering from a viral infection, a dangerous practice that can create antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Skinniness doesn’t necessarily equate to health
Skinny people tend to be viewed as healthy, largely thanks to the marketing efforts of the dieting and fitness industries.


Unfortunately, there are many ways to get skinny that will absolutely destroy your health, such as deliberately starving yourself or using fat burners.
Migraines aren’t just bad headaches
While many people believe that a migraine is simply an extremely painful headache, the two conditions are distinct, with a migraine involving large parts of the entire nervous system.


This is why migraines cause symptoms like nausea, sensitivity to light and visual disturbances, and it’s even possible to have a migraine with no pain.
Eggs aren’t bad for you
High cholesterol levels can lead to a number of negative health outcomes, and - since eggs are incredibly high in cholesterol - it’s widely assumed that they should be avoided.


In reality, eggs don’t have much of an impact on levels of cholesterol in the blood, and they’re packed full of healthy nutrients.
Pain doesn’t always equal gain
If you’ve ever set foot inside a gym, there’s a strong chance you’ve heard the phrase: “no pain, no gain.”


While it’s certainly a catchy mantra, it’s also terrible advice with no grounding in sports science, and it’s likely to lead to injury.
Healthy teeth aren’t shiny and white
The increasing prevalence of cosmetic treatments has led to the widespread belief that teeth should be sparkling white throughout your entire life.


In reality, even healthy teeth get stained over time, and bleaching products used to whiten them can come with health effects.
Running on a treadmill isn’t better for your knees
Running is notoriously hard on the knees, and many people try to mitigate the damage by running on a treadmill instead of pounding the pavement.


Unfortunately, research has shown that the surface you’re running on doesn’t actually have much of an impact on joint damage.
Yoga isn’t necessarily good for chronic pain
Conditions that cause chronic pain - such as fibromyalgia - can make it difficult to exercise, and sufferers are often advised to try yoga.


However, yoga really isn’t as gentle as it’s often made out to be, and it can actually worsen pain due to the strain it places on muscles, tendons and ligaments.
Six packs aren’t the pinnacle of fitness
Many people assume that six-pack abs are a surefire sign of superior strength and athletic prowess, but this really isn’t the case.


The only determining factor when it comes to visible abs is body fat percentage, meaning you can have a chiseled six pack while being malnourished.
You don’t lose most of your body heat through your head
It’s often claimed that you should wear a hat when it’s cold, because you lose most of your body heat through your head. In reality, hats just keep your head warm.


You actually lose heat at a steady rate across your entire body, and it's important to wear generally warm clothing if you're in the cold.
You can’t always tell if you’re working out too hard
Most gym goers assume that as long they feel okay during their workouts, they’re probably not pushing themselves too hard.


However, the pain from an overworked muscle can show up days after your workout, meaning you can injure yourself without realizing.
Alcohol doesn’t improve sleep
Having a drink or two before bed can definitely make it easier to drift off, but it will also ruin the quality of your sleep.


Additionally, if you come to relying on alcohol to fall asleep, this dramatically increases your risk of developing alcohol dependence.
Fat can be unhealthy
In recent years it’s become widely understood that sugar is actually far more harmful than fat. Unfortunately, this in turn has led to some misconceptions that fat is healthy.


While certain types of fat are healthy in moderation, they can still cause severe health problems if over-consumed, and many forms of fat are always harmful.
Eating less isn’t the best way to lose weight
Since the basic logic behind weight loss is to burn more calories than you consume, many people simply try to eat less food when they’re on a diet.


Unfortunately, this often isn’t an effective strategy, and dieters should instead focus on changing the types of food they eat, rather than the quantities.
You don’t need to “cleanse” your body
In recent years, “cleanse” has become one of the hottest buzzwords used by the health industry, with companies offering a variety of products that claim to remove toxins.


Your body is actually incredibly capable of removing toxins on its own, and most cleaning products are worthless at best, actively harmful at worst.
You should never suck venom out of a snake bite


Attempting to suck the venom out won’t help them at all, and you’ll likely poison yourself in the process. Instead, you should of course seek immediate medical attention.
Almost everyone needs between seven and eight hours of sleep
Despite the fact that scientists have long recommended that everyone get between seven and eight hours of sleep a night, a lot of people think they can function on less.


However, studies have shown that sleeping less than seven hours impacts cognitive performance, and can lead to serious health issues including cardiovascular problems, obesity, diabetes and more.
Coffee won’t sober you up
A cup of strong coffee is often touted as a way to help you sober up after excessive alcohol consumption. Alas, this will do nothing but increase risk of dehydration.


Unfortunately, the only way to sober up is to wait for your body to process the alcohol in your blood. Drink plenty of water instead.
You can get a good workout without breaking a sweat
Fitness enthusiasts tend to believe that you’re not really working out unless you’re breaking a sweat, but this isn't necessarily the case at all.


However, some individuals simply don’t perspire much, and they might risk dehydration and injury trying to work up a sweat during a workout.
Humans are capable of processing dairy
According to a widely circulated claim, humans haven’t been consuming dairy for long enough as a species for our bodies to adapt to it.


However, while at least half of the human population is lactose intolerant to some degree, for many people dairy is a healthy source of important nutrients.
Hot baths shouldn’t be used to treat hypothermia
Hypothermia is incredibly serious, and it can easily prove fatal. Since the condition is caused by the cold, it might seem logical to place a sufferer into a hot bath.


However, this can send them into shock or - in extreme cases - cause a heart attack. Instead, rewarm them gently and gradually, using blankets and clothes.
It isn’t normal to snore
Snoring is a common problem. It’s so common, in fact, that many people believe it’s completely normal to snore every night.


This isn’t the case, and snoring is often caused by an underlying health condition. Studies have also found that snorers are more likely to develop a number of serious diseases.
You shouldn’t pee on a jellyfish sting
The classic advice when it comes to treating jellyfish stings is to pee on the affected area. The rationale is that urine contains compounds that can neutralize the sting.


Sorry to say, but this isn't true. The best way to treat a jellyfish sting is to rinse it with vinegar, although if none is available saltwater can be used.
Stretching doesn’t warm you up for a workout
Thoroughly warming up before a workout is important for injury prevention, but performing a few static stretches really won’t cut it.


In fact, you should only start stretching after you’ve already warmed your muscles up with a series of gentle dynamic movements.
Turkey won’t help you sleep
Turkey is high in an amino acid called tryptophan. As this acid is related to serotonin, which can make you feel sleepy, some say eating turkey can help you sleep.


In reality, the amount of tryptophan in turkey won’t impact your serotonin levels, and eating before bed is an unhealthy habit that can increase the risk of obesity.
Being flat footed doesn’t increase your risk of injury
For years, it was assumed that flat feet increased the risk of injury, and flat-footed people were even disqualified from joining the military.


Recent research has actually suggested the opposite might be true, with one study finding that flat-footed Israeli soldiers were less prone to injury.
Alcohol doesn’t warm you up
The phrase “beer jacket” refers to feeling warmer after consuming alcohol. In reality, you actually lose heat faster when you’ve been drinking, due to your blood vessels dilating.


This phenomenon can have fatal results, with revelers suffering from hypothermia after underestimating how cold it is whilst under the influence.
Lyme disease doesn’t always cause a target-shaped rash
Lyme disease is generally transmitted by infected ticks, and its symptoms can be debilitating. Oftentimes, tick bites result in a telltale rash that looks like a target.
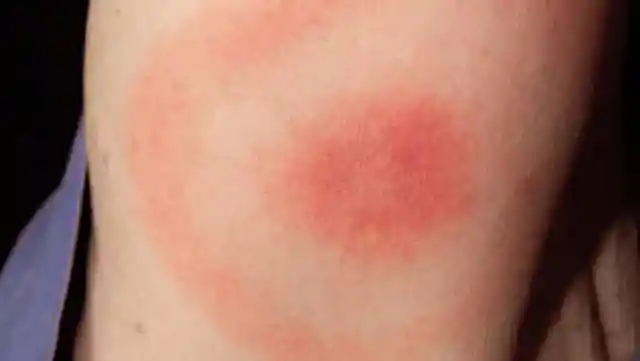
This rash doesn't always show up, however, and medical treatment should be sought immediately any time you've been bitten by a tick.
You shouldn’t try to make yourself vomit after ingesting poison
If you believe you’ve accidentally ingested a poisonous substance, it’s tempting to try and make yourself vomit. Studies have shown, however, that inducing regurgitation doesn’t actually improve outcomes in poisonings.


Instead, it actually increases the risk of damaging internal tissues. If you've ingested a harmful substance, dilute it by drinking lots of water.